Introduction
Metal engraving is a time-honored craft that blends art and science, transforming plain metal surfaces into intricate works of art. Whether for functional purposes like marking tools or for artistic endeavors such as jewelry design, metal engraving plays a crucial role across various industries. This article will explore both traditional and modern engraving techniques, highlighting their applications, tools, and tips for beginners. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of how to choose the right method and the right engraving machine for your project, whether you’re etching by hand or using advanced laser technology.
Traditional Metal Engraving Techniques
Hand Engraving
Hand engraving is the oldest form of metal engraving, involving the use of specialized tools such as burins and gravers to carve designs directly into the metal by hand. This technique requires great skill and precision, as each stroke is permanent. Hand engraving is often used in high-end jewelry, fine arts, and custom creations. The depth and detail achieved through hand engraving give the final product a unique, handcrafted quality that is highly prized.
Etching
Etching is another traditional technique that uses chemical processes to engrave metal surfaces. The most common method involves coating the metal with a resist, such as wax or varnish, and then using an acid or another corrosive substance to eat away the exposed areas, creating the design. Etching can be done on a variety of metals, including steel, copper, and brass, and is often used in printmaking, decorative arts, and creating detailed patterns on firearms and other metal objects. The process allows for fine, intricate designs that are difficult to achieve with hand engraving.
Modern Metal Engraving Techniques
Laser Engraving
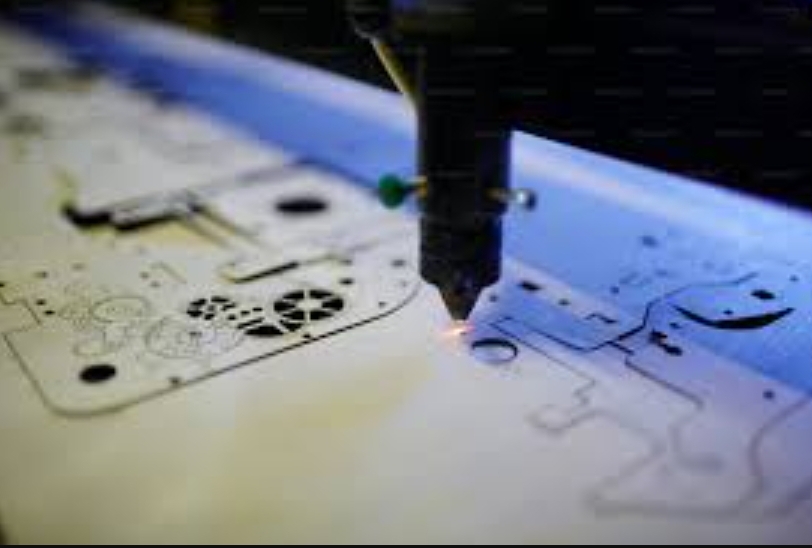
Laser engraving has revolutionized the metal engraving industry by providing a method that is both precise and efficient. This technique uses a high-powered laser to heat the metal surface to its boiling point, effectively vaporizing the material to create deep, permanent marks. The advantage of laser engraving over traditional methods is its ability to produce highly detailed and consistent designs quickly, making it ideal for large-scale industrial applications as well as intricate artwork. Laser engraving is widely used in industries like jewelry making, electronics, and automotive manufacturing due to its versatility and precision.
Laser Etching vs. Laser Engraving
While often used interchangeably, laser etching and laser engraving differ significantly in their processes and results. Laser etching involves heating the metal surface to a point where it melts and expands, creating a raised mark without removing material. This method is typically used for marking metal surfaces with barcodes, serial numbers, and logos where depth isn’t a requirement. On the other hand, laser engraving removes material to create deeper, more permanent marks. Choosing between etching and engraving depends on the desired depth and durability of the mark, as well as the material being used.
Choosing the Right Technique
Factors to Consider
Selecting the appropriate engraving technique depends on several factors:
- Material Type: Different metals react differently to engraving methods. For example, softer metals like aluminum may be better suited for laser etching, while harder metals like stainless steel are ideal for deep engraving.
- Desired Outcome: The depth, clarity, and permanence of the engraving are crucial considerations. Laser engraving is typically preferred for deeper, more durable markings, while etching is better for surface-level designs.
- Cost and Accessibility of Tools: Hand engraving requires a high level of skill and practice, while laser engraving, though initially more expensive due to the cost of machinery, offers ease of use and consistency, making it more accessible for large-scale projects.
Laser Engraving Machines
Modern laser engraving machines are the backbone of contemporary engraving processes. These machines vary in size and power, but typically fall into three categories:
- CO2 Lasers: Ideal for non-metal materials but can also be used on coated metals.
- Fiber Lasers: The fiber laser machines are the most common for metal engraving, offering high precision and deep engraving capabilities.
- Diode Lasers: Less powerful but more affordable, suitable for small-scale or hobbyist projects.
When selecting a laser engraving machine, consider factors such as the type of laser, power output, bed size, and software compatibility.
Tools and Equipment for Metal Engraving
Hand Engraving Tools
Traditional hand engraving requires a set of specialized tools designed for precision and control. Common tools include:
- Burins and Gravers: These are the primary tools used to cut into the metal, each with a different shape and size for various effects.
- Chisels and Hammers: Used to create deeper cuts and larger designs, particularly in harder metals.
- Sharpening Stones: Essential for maintaining the sharpness of the engraving tools, ensuring clean and accurate cuts.
Tips for Beginners
Getting Started with Hand Engraving
For those new to hand engraving, starting with basic techniques and practice is key. Beginners should focus on mastering the use of burins and gravers on softer metals like copper or brass. It’s important to practice steady hand control and consistent pressure to achieve clean, precise lines. As skills develop, more complex designs and harder metals can be attempted. Engraving classes or tutorials can be invaluable for learning the nuances of this craft.
Starting with Laser Engraving
For beginners interested in laser engraving, choosing the right entry-level machine is crucial. Look for a machine that offers user-friendly software, adjustable power settings, and safety features. It’s also important to understand the material compatibility and to start with simple designs to become familiar with the engraving process. Safety is paramount, so always use appropriate protective gear, such as safety glasses, and ensure proper ventilation when operating laser machines.
Conclusion
Metal engraving is a versatile and enduring art form that bridges the gap between tradition and technology. Whether you’re drawn to the tactile precision of hand engraving or the high-tech efficiency of laser engraving, the techniques and tools available today offer endless possibilities for creativity and functionality. As technology advances, metal engraving continues to evolve, opening up new opportunities for innovation in both artistic and industrial applications. The future of metal engraving is bright, with trends pointing towards even more sophisticated and accessible tools for both professionals and hobbyists alike.